Gout Treatment in Bangladesh
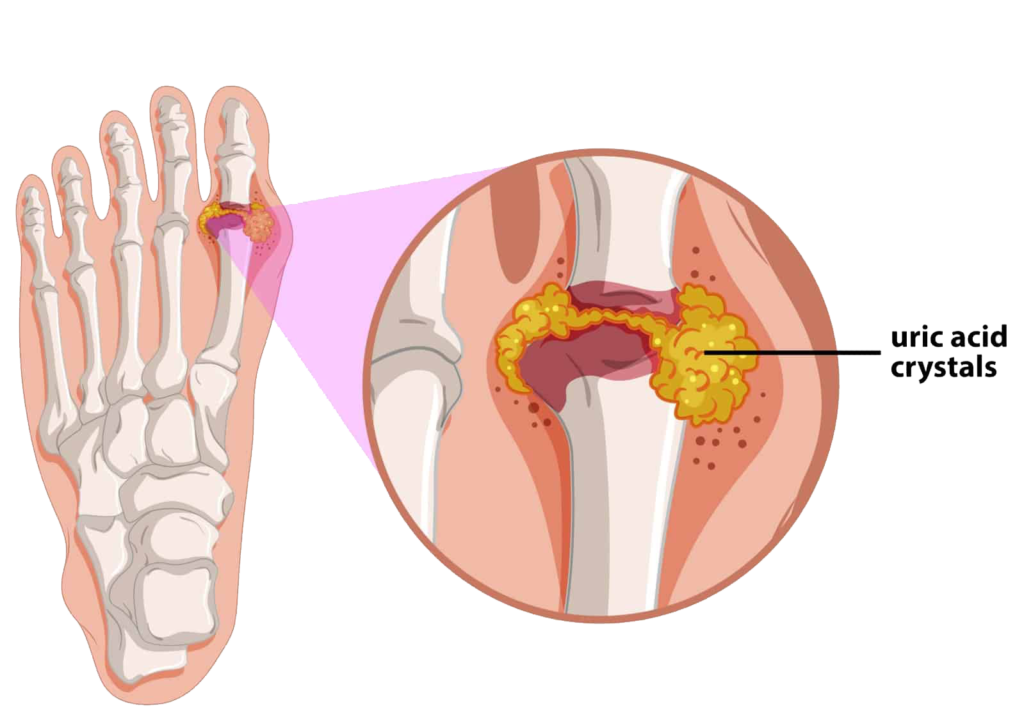
Gout is a type of arthritis that develops when there is an increase of uric acid levels in your body. Due to high uric acid levels, urate crystals start to form in the joints, triggering inflammation and excruciating pain. Gout attacks can be unbearably painful, making even the slightest movements challenging. It could be tough to find a comfortable position since it might seem like the affected joint is on fire. Moreover, the attacks can go on for days, leaving the victim worn out and depleted.
Having gout disease can also lead to emotional stress. Although others might not fully understand the severity of the pain and the constraints of the condition, patients may feel frustrated and alone. They could feel upset and unhappy that they cannot participate in activities with their loved ones or hobbies they used to enjoy.
“Overall, gout can be a challenging condition, both physically and emotionally,” says Dr. Monzur Khoda, a renowned rheumatologist in Dhaka, Bangladesh. “However, with proper management and treatment, many gout patients can lead fulfilling lives.
Gout Treatments
Therapy for gout typically consists of a combination of lifestyle modifications and medications.
Lifestyle modifications: 
- consuming a lot of fluids to wash away uric acid
- abstaining from alcohol and sugar-sweetened beverages
- uric acid food to avoid include red meat, seafood, and organ meats
- maintaining a healthy weight
Medications: There are several medications used to treat gout, including:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate pain and swelling during a gout attack.
- corticosteroids to reduce the swelling
- colchicine to ease the pain as well as inflammation
- urate-lowering therapy (ULT) to help reduce the uric acid levels in the blood to prevent future gout attacks

Surgery: In rare circumstances, managing gout may require more than dietary adjustments and medication. The doctor may advise gout surgery to remove tophi or repair damaged joints in severe situations or cases with frequent gout bouts, joint injury, or tophi production.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Monzur Khoda.
Gout treatment cost in Dhaka, Bangladesh
As with any surgery or medical procedure, the gout treatment cost in Dhaka, Bangladesh, can fluctuate depending on several variables.
In Bangladesh, gout is often treated with medication, lifestyle changes, and surgery if need be. The precise drug recommended and the kind of surgical treatment will determine the cost of both pills and surgery.
For instance, the monthly cost of urate-lowering medication can range from BDT 500 to 3000 (USD 6-35), while the price of a colchicine tablet can range from BDT 25 to 100 (USD 0.30 to 1.20).
Symptoms of Gout
symptoms of gout typically involve sudden and severe joint pain, often affecting the big toe. Here are some common symptoms of gout:
- Intense Joint Pain: Gout usually manifests as sudden and severe joint pain, commonly starting in the big toe. The affected joint may become tender, swollen, and extremely sensitive to touch or pressure. The pain can be excruciating and may develop rapidly, often at night.
- Redness and Swelling: The affected joint may appear red, swollen, and inflamed. The swelling can cause the joint to feel hot to the touch and make it difficult to move the affected area.
- Limited Range of Motion: Due to the pain and swelling, the range of motion in the affected joint may be limited. Movement may exacerbate the pain, making it challenging to perform regular activities.
- Tophi Formation: In advanced cases of gout, urate crystals can accumulate and form small, firm lumps under the skin called tophi. These tophi usually develop in joints, fingers, elbows, and the outer ear. Tophi may cause deformities and chronic joint damage if left untreated.
- Recurring Attacks: Gout often follows a pattern of recurrent attacks, with symptoms subsiding after an initial episode, only to resurface weeks, months, or even years later. The frequency and severity of these attacks can vary among individuals.
- Limited Joint Mobility: Over time, repeated gout attacks and persistent inflammation can lead to joint damage, potentially resulting in reduced mobility and chronic joint stiffness.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Monzur Khoda.
Causes of Gout
A buildup of uric acid in the body can form urate crystals in the joints, which in turn can cause gout. The appearance of gout symptoms, such as redness, pain, and inflammation, results from your body’s inflammatory response to the urate crystals.
Several factors can contribute to high levels of uric acid, including:
- Diet: Eating purine-rich foods and drinks like red meat, seafood, and alcohol can raise uric acid levels.
- Medical issues: Some medical conditions, like diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney impairment, can make you more likely to get gout.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including aspirin and diuretics, can raise uric acid levels and cause gout symptoms.
- Age: Gout affects older persons more frequently, with the risk rising if you are over 45.
- Joint injury: Damage or surgery to a joint can raise the risk of getting gout in that joint. Having one or more of the risk factors, like age or gender, does not necessarily mean that you will develop the condition.
“If you have any risk factors, and notice early symptoms such as joint pain, swellings, and redness, do not prolong seeking medical aid,” cautions Dhaka’s prominent rheumatologist, Dr. Monzur Khoda. “Getting medical intervention to facilitate uric acid control is crucial; otherwise, it can lead to further complications.”
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Our body generally expels a waste product called uric acid in the urine. However, in gout sufferers, the body either creates too much or has trouble getting rid of it. The accumulation of uric acid crystals in the body’s tissues and joints leads to gout. This results in the buildup of uric acid crystals in the tissues and joints, which results in discomfort and inflammation.
Gout is characterized by sudden, excruciating pain, redness, and swelling in the afflicted joint. The skin over the joint may also feel heated to the touch and appear glossy and stretched.
Gout is often identified through a combination of laboratory tests, physical examination, and medical history. In addition to imaging procedures like X-rays or ultrasounds to assess joint damage, your doctor may order blood tests to analyze uric acid levels.
The preliminary criteria outlined by The American College of Rheumatology to diagnose gout calls for the presence of one of the following:
- Monosodium urate crystals in synovial fluid
- Tophi confirmed with crystal examination
Gout cannot be cured, but you can effectively control it with medication and dietary changes. Most gout sufferers may manage their symptoms and avoid recurrent bouts with the proper care.
